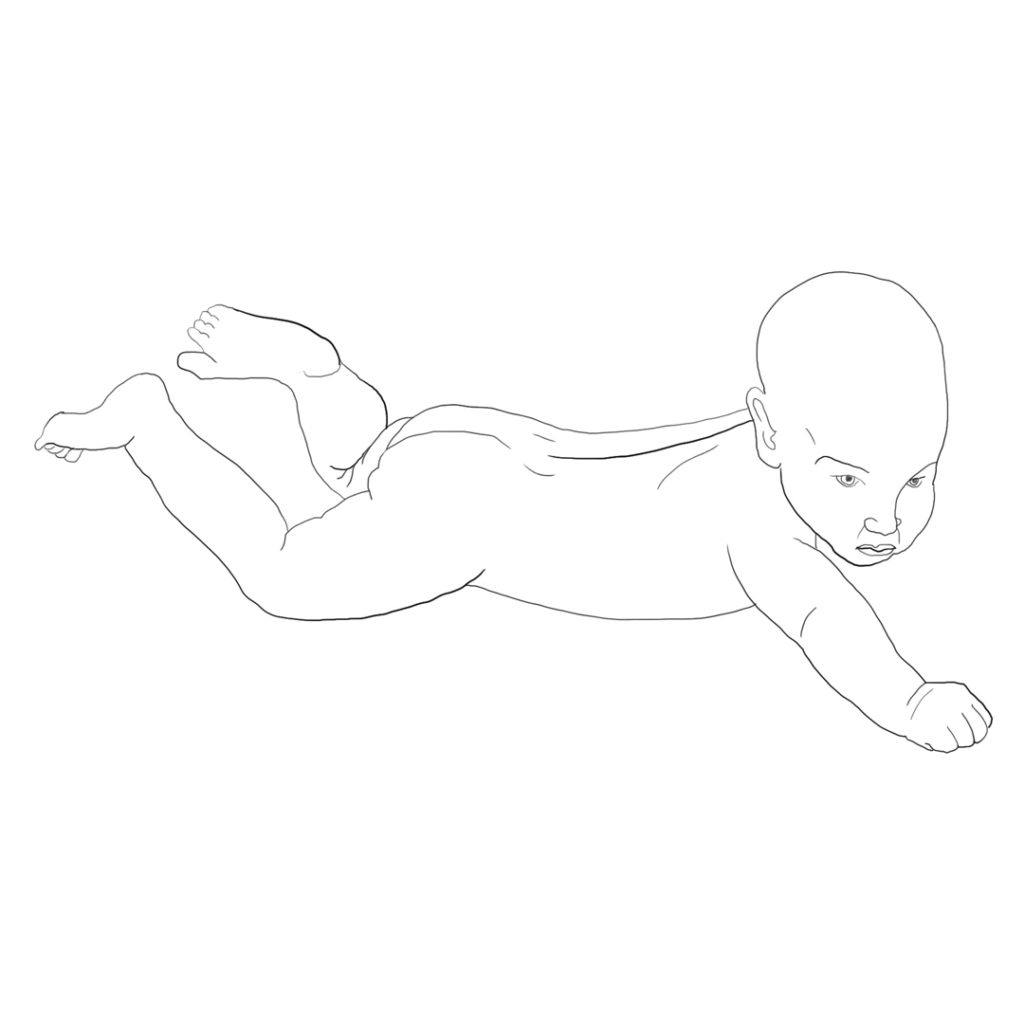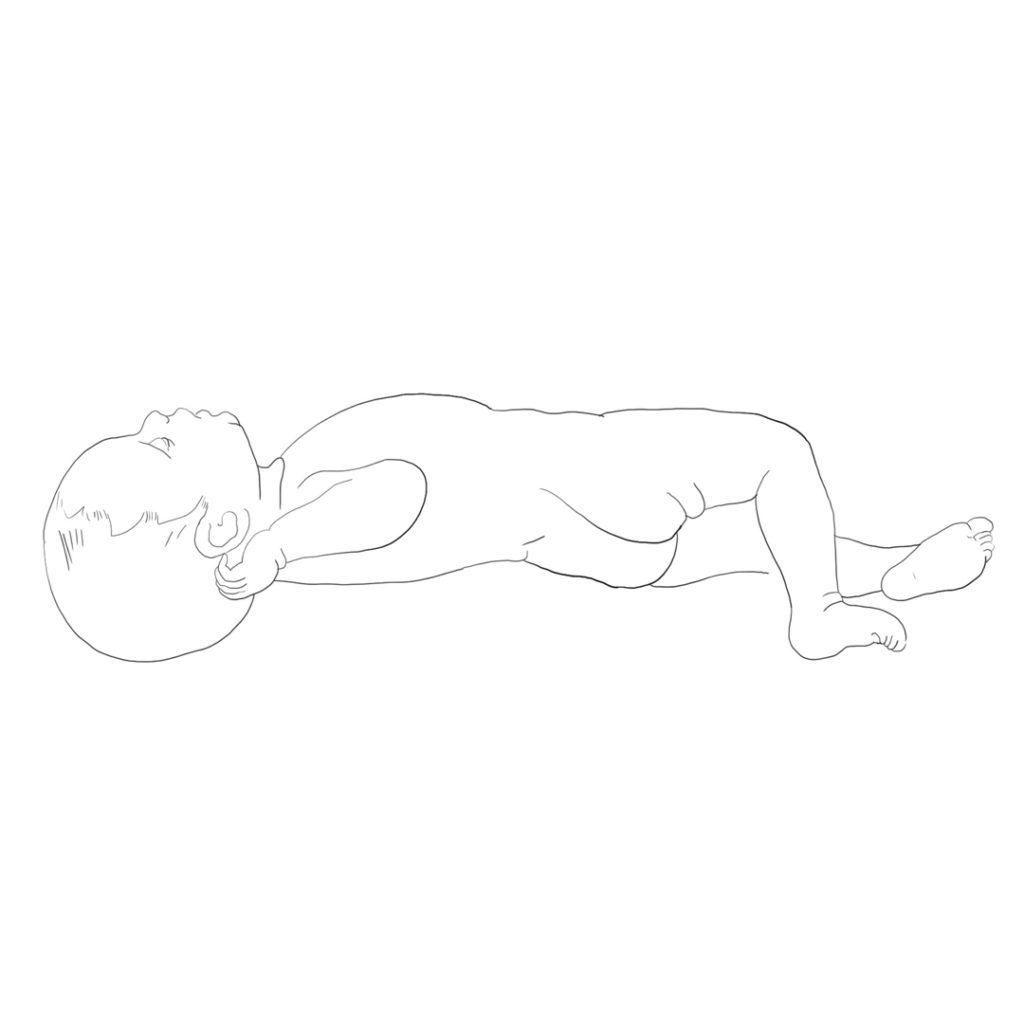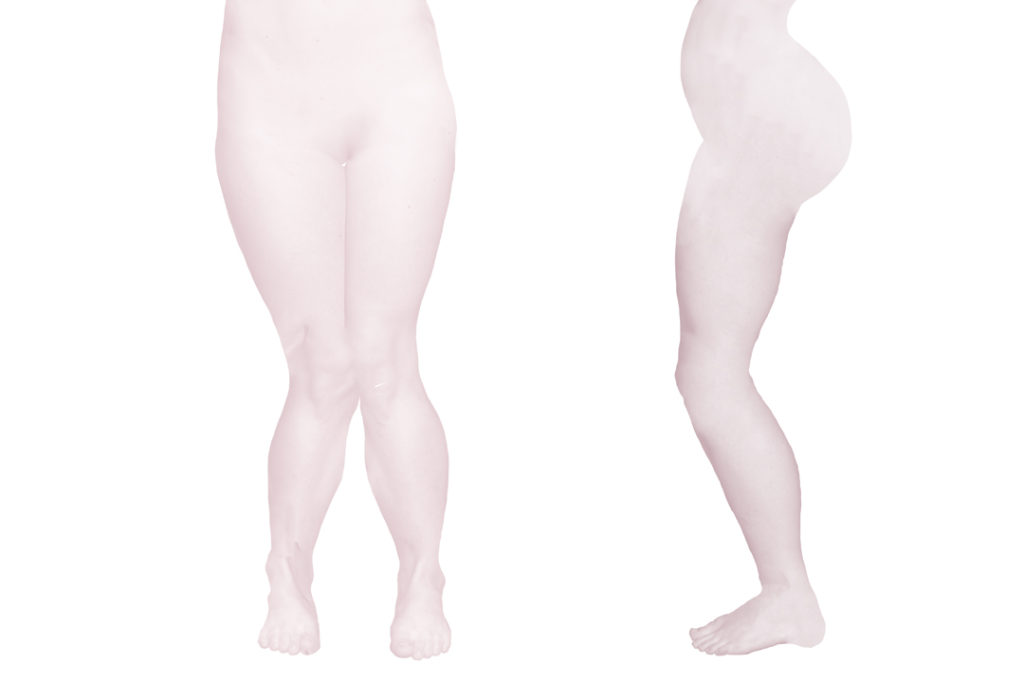
The pathology of motor development is most pronounced in the disturbance of the ability of physiological extension and the associated rotation of the spine. The subsequent impact of impaired development is pronounced within the normal range of rotation in the root joints (shoulder and hip joints). Further, this impairment spreads into the acral joints of the limbs. That’s how the major pathological change originates in the global motor skills of the body.
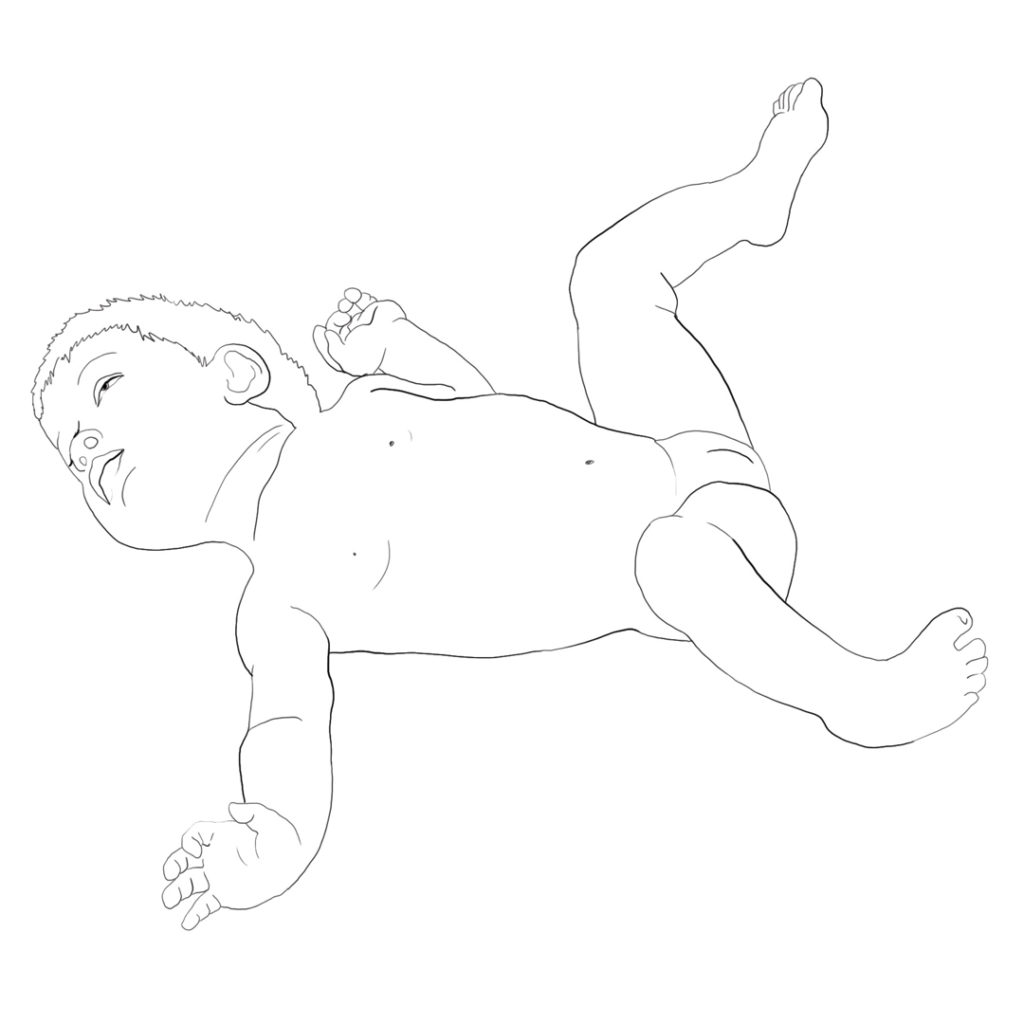

Disorders of autonomic regulation of the joint centration are manifested as follows:
- Disorder of autonomic joint centration, in terms of both static and dynamic centration
- Predominance of inner rotation, particularly in root joints
- Predominance of adduction, most noticeable in the hip joints
- Predominance of flection
- Predominance of ulnar deviation in the posture of the hand
- Restriction of supination of the forearm
- Restriction of physiological range of motion in the joint
- Gradual development of joint subluxation or luxation, most often in hip joints
- Impaired anterior head posture
- Impaired posture of the mandible, most often in the retrogenia
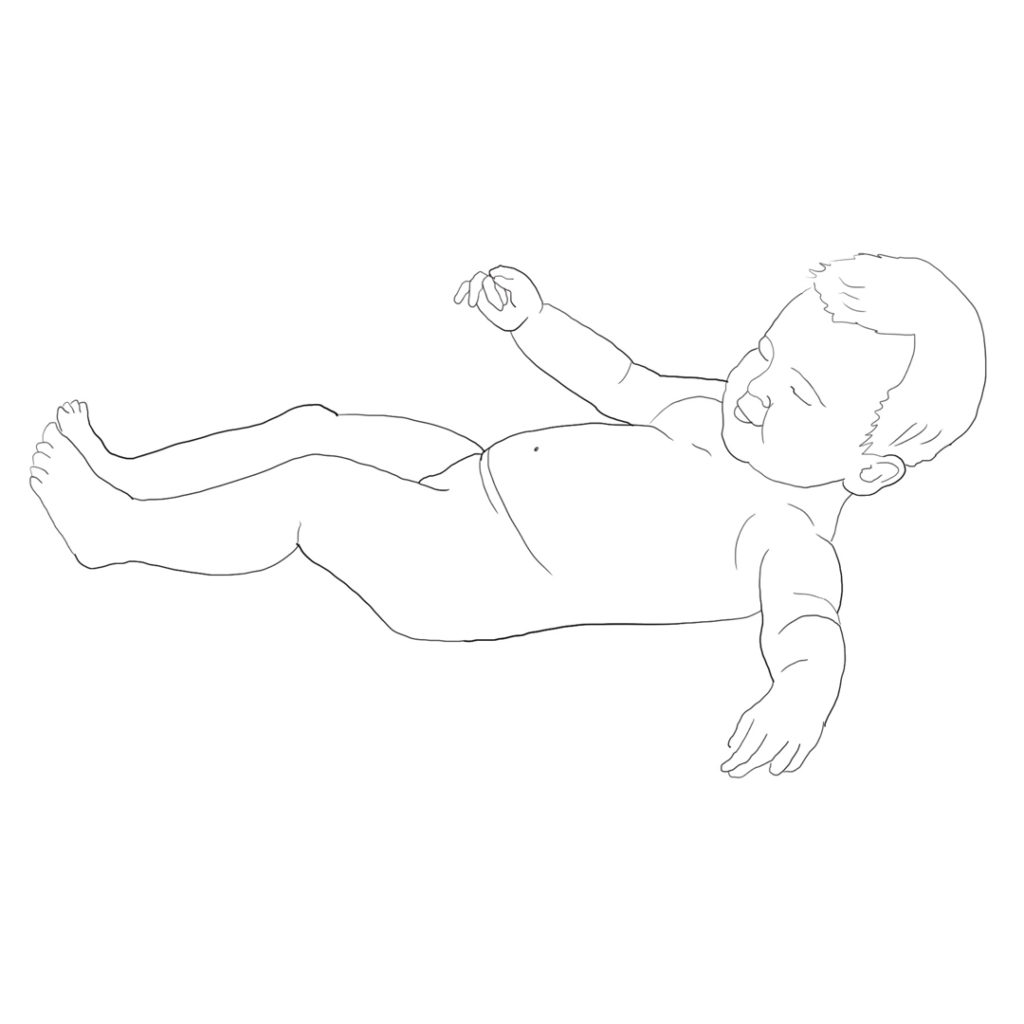
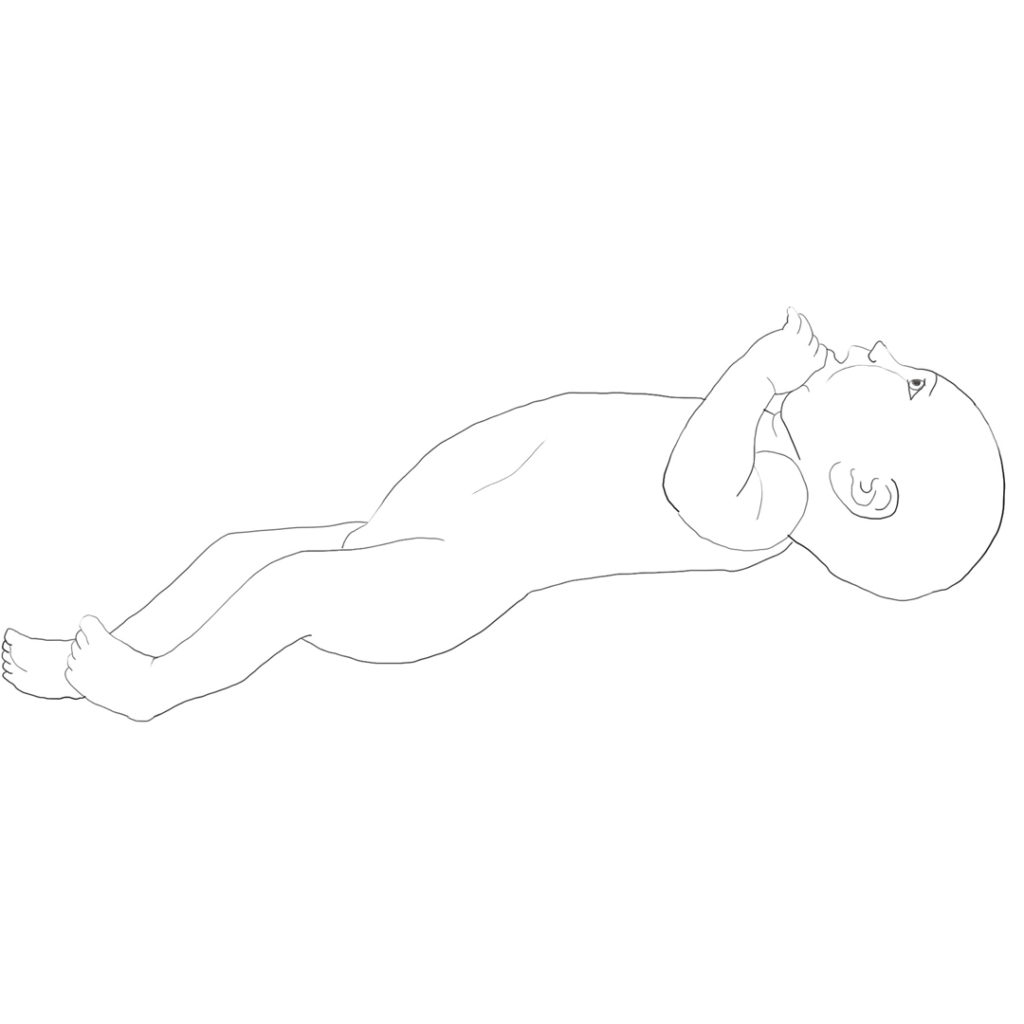


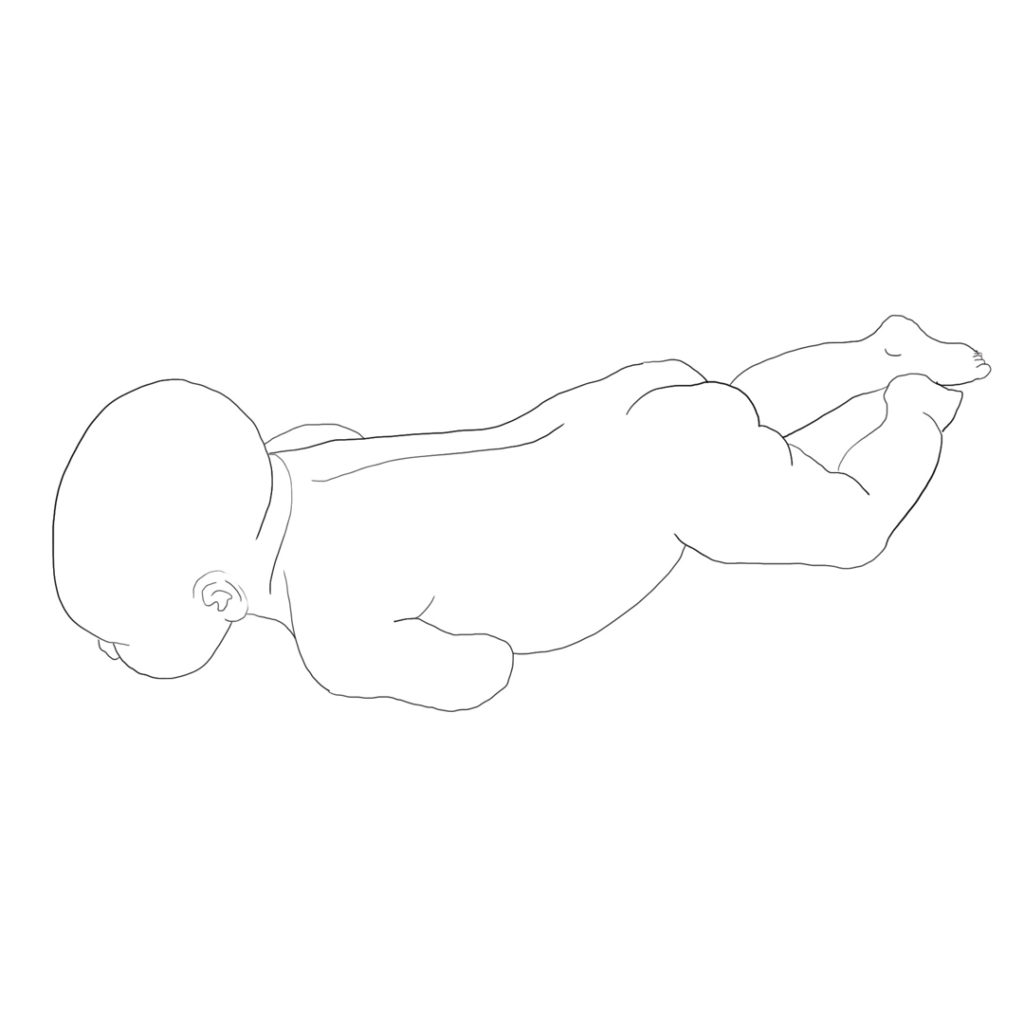
Musculoskeletal disorders are visible in the incorrect posture of the body at all levels:
- Collapse of the arches of the feet
- Deviation of the axes of calcanei and tarsal bones and digits
- Deviation of the axes of feet on the inner side
- Deviation of the axes of the long bones of the lower limbs
- Deviation of the axes of the knees
- Inner rotation in the hip joints with relative shortening of the lower limbs.
- Lateral tilting of the pelvis
- Axillar rotation of the pelvis
- Flection posture of the pelvis causing functional shortening of the lower limbs, and its rotation
- Hyperlordotic posture of the lumbar spine
- Lateral deviation of the axis of the lumbar spine
- Axillar rotation of the axis of the lumbar spine
- Hyperkyphotic posture of the thoracic spine
- Impaired configuration of the chest
- Impairment of the spinal axes
- Impaired postures of the shoulder girdles in an uneven height and in the protraction
- Impairment of the stereotypical respiratory movement
- Impaired configuration of the chest
- Impairment of the autonomic posture of the lower limbs and the left hand
- Severe disorders of the autonomic regulation of the posture of the body
- Immediate change in the autonomic posture after the therapy
- Impairment of the autonomic regulation of the basic stereotypical movements
Gait
Grasp
Respiratory movements
Orofacial stereotypical movements
Swallowing
Chewing
- Impaired dental occlusion
- Impaired development of speech, singing, playing the wind musical instruments